
Context : Artificial intelligence has revolutionized the daily lives of many people in recent years: texts, images or videos, everything is possible with AI.
Artificial intelligence is disrupting our daily lives and is transforming the work of many professionals: texts, images and videos generation, analysis… Sometimes, it feels like anything is possible with AI. And the job of Strategic Analyst is also affected.
In an era where a simple prompt seems capable of replacing hours of work and analysis, it is crucial to understand the stakes involved. Discover the risks associated with this rapidly expanding creative force across the world, as well as the opportunities it offers for the intelligence process.
Here, we are focusing on generative artificial intelligence. However, other types of AI can also be integrated into intelligence processes. This includes recommendation systems for articles and sources, fake news detection, or the identification of duplicates and highly similar contents. These intelligent agents provide valuable support to intelligence teams.
Be critical with the results provided by artificial intelligence,
it is up to you to determine the credibility of the statements, as AI blurs reference points!
Almost every stage of the Strategic Intelligence cycle can benefit from generative artificial intelligence. 🔄
It plays a role both upstream (sourcing) in the process and in data processing (analysis et data visualization) and downstream (dissemination). Upstream, AI assists in collecting and identifying new sources, and in validating them based on multiple criteria (SEO, reviews and comments, number of published articles, website structure…). At the analysis stage, it facilitates the writing of summaries based on the most relevant information. And regarding dissemination, AI helps to tailor intelligence deliverables (newsletters and reading portals) to the needs of the end user and automates processes. It provides thus significant time and efficiency gains. ⏱️
Today, many are the information professionals to take a keen interest in the promises of AI.
Applied to Web-based content, artificial intelligence provides valuable insights about the market and businesses : their economic impact, their geographical implentations, their investments, their suppliers, their innovations, their products…
AI helps prioritize information by detecting keywords and can establish relationships between dispersed words in a text. It also plays a role in automating filters that reduce the time intelligence professionals spend on low-value-added tasks, including when dealing with textual data in languages other than French. Finally, we can add its capability to categorize information flows by grouping them based on contexts, economic sectors, countries, or markets.
As we can see here, artificial intelligence has more than one advantage to showcase
in helping intelligence professionals accomplish their missions!
Learn more: Unlock the potential of Strategic Intelligence with generative AI
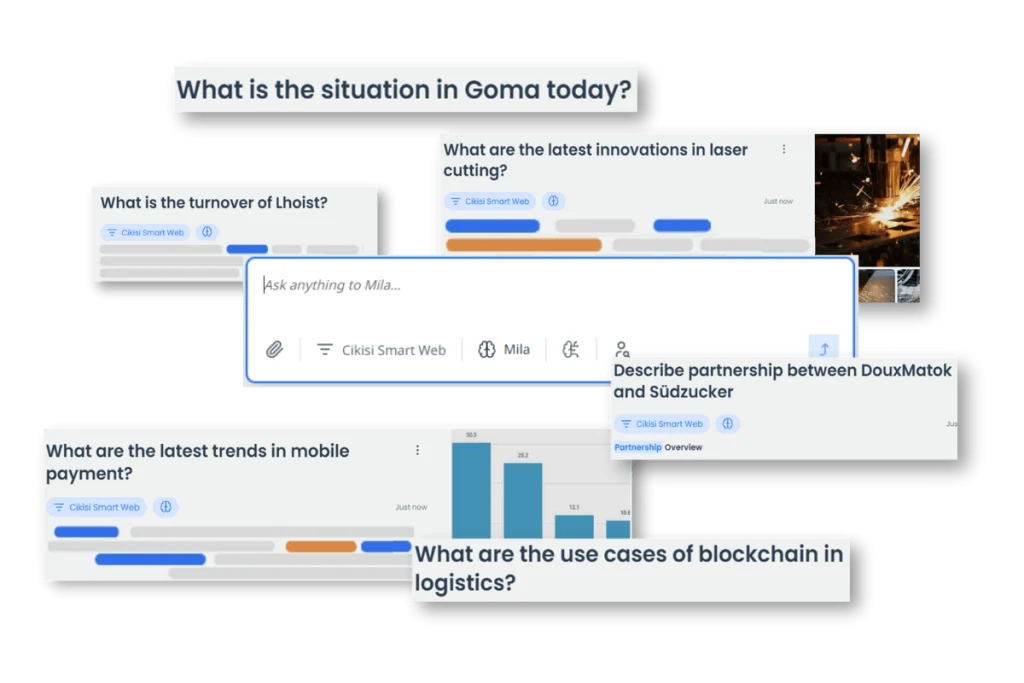
Cikisi’s AI and its chatbot, Ask Mila, might be the solution: its database updates every hour, it analyzes a maximum number of sources provided with each query, and it produces zero hallucinations.
Discover the Cikisi’s chatbot: 👉 Ask Mila
In addition to these features, Ask Mila integrates article recommendations. When a team member likes or dislikes an article, our AI increases or decreases the score of both the article and its information source. As a result, the “quality score” of the article – information source – evolves based on this “scoring system”.
Ask Mila greatly assists in identifying credible sources, crossing information and evaluating a source.
You now know a lot about generative AI : the risks it entails and the benefits it provides. It’s up to you to weigh the pros and cons of the tool you use to make the right decisions.
Don’t forget: In strategic intelligence, the accuracy of the collected information is key!
Contact us now and discover our all-in-one solution: